Precision Farming
The practice of Precision Farming has been enabled by the advent of GPS and GNSS.
The farmer's ability to locate their precise position in a field allows for the creation of maps showing spatial variable data of anything that can be measured, to include crop yields and quality, terrain features, moisture and nutrient levels, and light reflectance for chlorophyll levels and NDVI maps.
Variable Rate Technology (VRT) like seeders, sprayers, etc., are programmed to utilize the information for greatest economic and environmental benefit. Precision agriculture aims to optimize field-level management with regard to...
Controlled Traffic Farming
Controlled traffic farming turns our present production systems on their head by leaving 80 – 90% of fields permanently without compaction, rather than the other way around.
CTF aims to confine soil compaction to the least possible area of permanent traffic lanes. It sounds simple but because our machines have never been designed to do this, it needs a lot of thought and good planning to get it right
The LearN & Auto-N Project
The ‘Chessboard Trials’ used in the Auto-N Project sponsored by DEFRA (LK09134) and HGCA (AHDB) was hosted by August Farms in Oxfordshire.
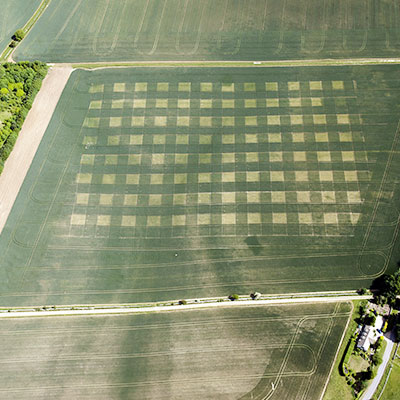

This project managed by ADAS ran between 2011 -2015 has transformed our understanding of nitrogen responses and shown the possibilities of ‘on farm’ spatial experimentation to understand how soil variability effects husbandry outcomes. These trials show that nitrogen may not be the cause of very large yield variations, so the quest to understand the causes of soil yield variation now becomes a priority for research.
"The family farm is going high-tech. From robotic milking machines to data-gathering drones, industry watchers say technology is making agriculture more precise and efficient as farmers push for increased profits and yields."

Links
- CTF Europe - Controlled Traffic Farming across Europe - June 2015
- Cover crops - definitely worth a second look... - Feb 2015
- Tillage - Spring 2015
- Potential of no till - 2014
- Innovate UK - Precision Farming Magazine - 2013
- Precision route to know the N2O.pdf - October 2013
- Controlled-traffic Farming in Oxfordshire - April 2010
